Masonry is a construction technique that creates a structure or wall with suitable construction materials. Bricks, stones and concrete blocks are some of the most widely used materials for construction. Stone and brick masonry are some of the common types of masonry works, and the evolution of blocks makes it a preferred choice in masonry works. Here we take a look at what solid block masonry is and everything you need to know about it.
What is Solid Block Masonry?
Solid block masonry is a construction technique that uses solid concrete blocks as the primary construction material. It is similar to brick masonry but uses solid concrete blocks instead of bricks to construct the structure. These masonry structures have high load-bearing capacity, are easy to build, and can survive for long periods of time.
Types of Solid Blocks
Fly Ash Block
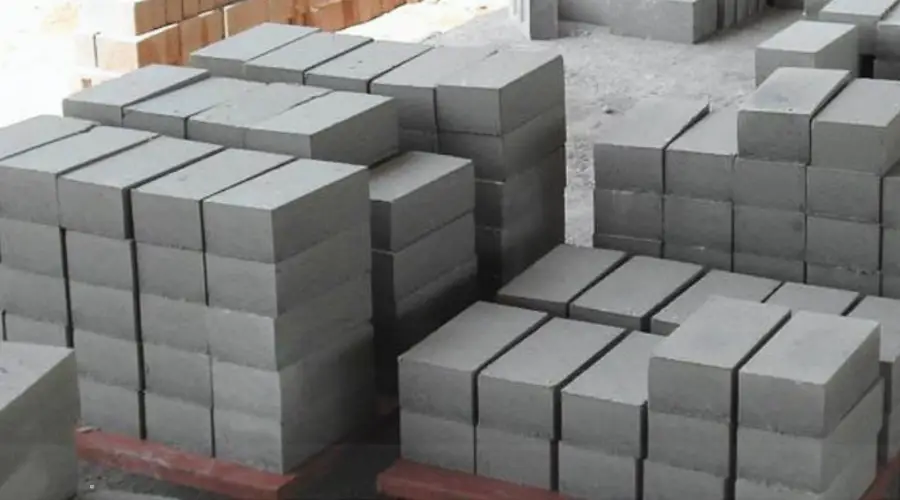

As the name suggests, these blocks are made with fly ash (extracted from burning coal). The fly ash is mixed with Portland cement and adequate water to make lightweight solid blocks. These blocks are eco-friendly, economical and help in rapid construction works.
Paving Block
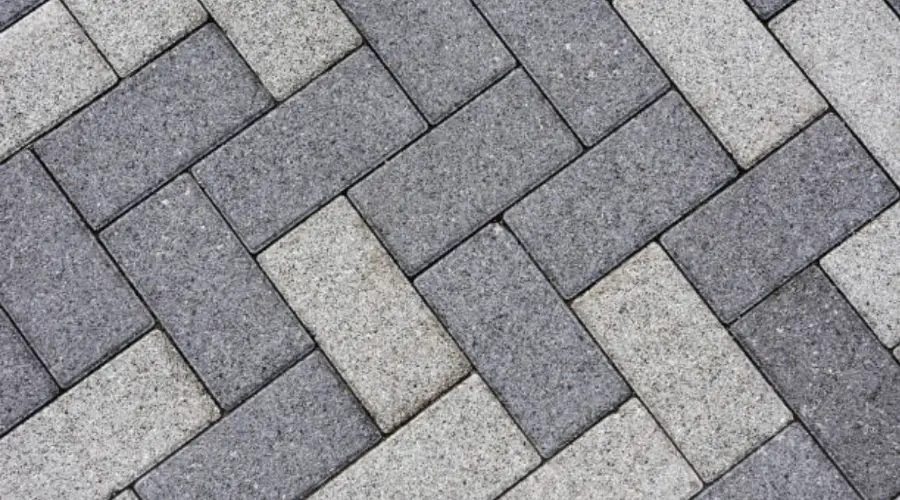

These blocks are primarily used for paving walkways, parking areas, and road shoulders. They come in various sizes and colours and are ideal for pavements in high-traffic areas, suitable for carrying live loads.
Cellular Lightweight Block
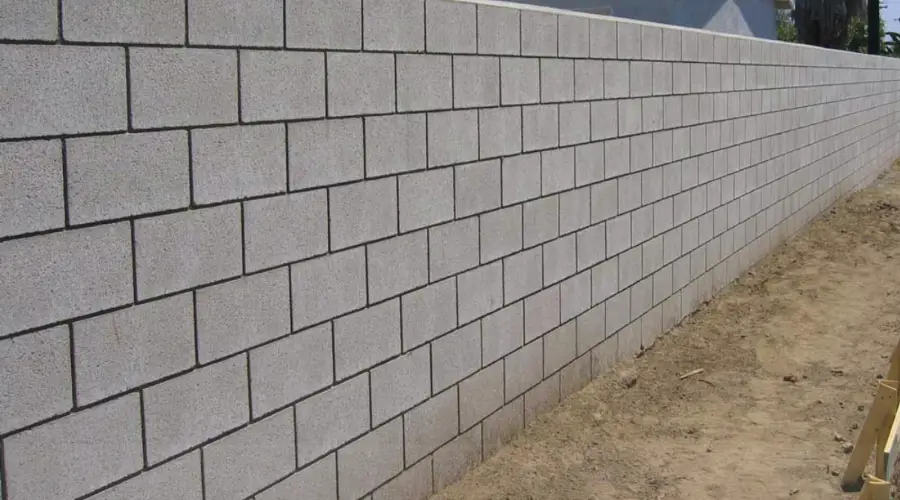

Cellular lightweight block is a lightweight construction material made from cement, foam, and fly ash. It is available in high-density and low-density blocks. The density determines the suitability for load-bearing and non-load-bearing structures.
Applications of Solid Block Masonry
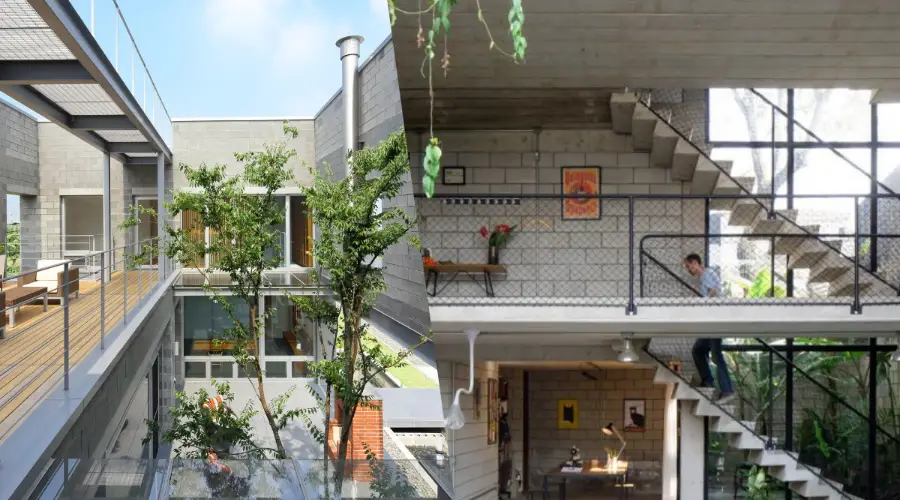

- Solid block masonry is suitable for constructing load-bearing interior and exterior structures.
- This block masonry work is ideal for almost all construction types, including residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
- Perfectly arranged solid block masonry can build retaining walls to stabilise the structure from landslides and soil erosion.
- Solid block masonry works are suitable for constructing attractive and durable garden walls, raised garden beds and other landscaping works where retaining moderate amounts of soil is required.
- Its soundproofing properties make it ideal for institutional and government buildings.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages
- These structures have high strength and durability, making them suitable for load-bearing structures and foundations.
- These structures act as a thermal insulator that helps maintain the room temperature.
- The size of the blocks is larger, reducing the construction time as a lesser number of blocks need to be laid to fill a space.
- The solid block structure provides acoustic insulation to the structure.
- Suitable for all types of construction, including residential, commercial and industrial buildings.
Disadvantages
- These blocks are heavier than bricks or hollow blocks, which increases the overall structural load.
- This masonry may not be as attractive as brick masonry or stone masonry walls when left exposed.
- Highly skilled labourers must carefully handle and install the wall to ensure its structural integrity.
- There is a high chance of water seeping through the buildings, as it is vulnerable to efflorescence and water damage.
- This masonry work can be expensive compared to other masonry works.
- Solid blocks are rigid and are prone to crack and damage, which limits their flexibility.
Mix Proportions of Mortar for Solid Block Masonry
The mortar mix proportions used for solid block masonry could vary based on numerous factors, such as purpose, external climatic conditions, and local building codes. However, the general mix proportions range from 1:3 to 1:6, meaning one part of cement is used for three to six parts of sand.
Solid Block Masonry Construction Process
- Prepare the mortar by blending cement, sand, or other adhesives with the appropriate amount of water.
- Blend all the raw materials with a suitable mix proportion for binding the blocks together.
- Choose the correct quality and quantity of the solid blocks required to construct the structure.
- Prepare the foundation by ensuring the surface is clean, dry, and level.
- Pour the mortar on the foundation to create a mortar bed before placing the first layer.
- Place the blocks on the mortar bed and apply mortar to the bed and vertical joints at each subsequent course.
- Use a spirit level and plumb bob to ensure that the blocks are accurately placed straight.
- After laying the first course, pour the mortar over it and arrange the blocks at half the width.
- Repeat the block-laying using the mortar and complete the wall, aligning alternate layers similarly.
Maintenance
- Regular inspection is key in maintaining the concrete blocks, as numerous environmental factors could affect their structure. Early detection and repair could improve their lifespan and efficiency.
- Practice effective cleaning methods such as using cleaning agents and pressure washing to remove unwanted elements damaging the blocks.
- Address any cracks or damages on time and seal or repair them before they become a big issue.
- To extend the structure’s lifespan, high-quality materials, proper installation, and coating can be used during construction and maintenance.
Conclusion
Solid block masonry is one of the most widely used masonry techniques in modern construction, especially for multi-storeyed structures. It is extremely strong and durable and can easily withstand heavy loads. Although heavy and costly, solid block masonry is worth the initial investment as it provides long-term benefits. Its numerous advantages have almost replaced the usage of brick and stone masonry. It would be no wonder if solid block masonry one day completely replaced brick masonry.