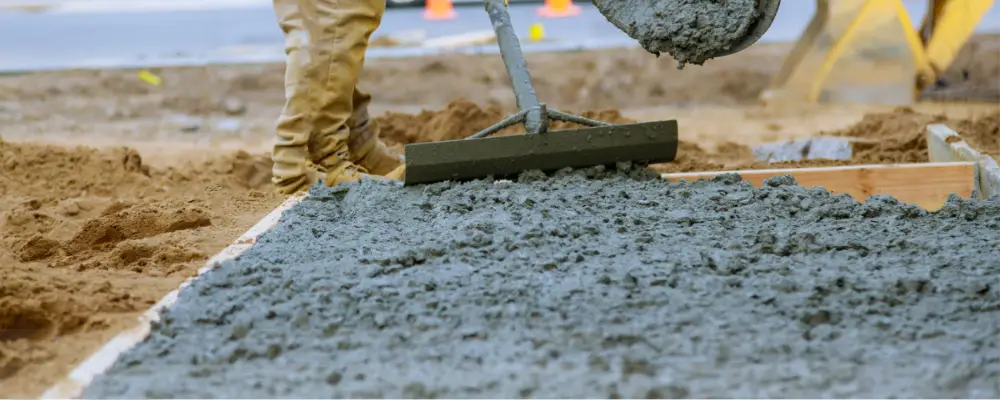
The choice of concrete mix is crucial for creating the right mixture for completing building and construction. A typical concrete mix that can be used across the construction field is cement, aggregate, water, and sand. Water can be added at different ratios for different purposes of construction. The project’s successful completion depends on choosing the appropriate water ratio for a given use. The advantages of mixing wet concrete, its uses, the mixing procedure, and the distinctions between wet and dry mixed concrete will all be covered in this blog.
What is Wet Mix Concrete?
Cement, aggregates, sand, and water are the ingredients of wet mix concrete. Typically, these combinations are transported to the construction site with mixers on big trucks. Wet pouring combines all ingredients, including water, in one place before delivering the finished mixture to the building site. Since the concrete truck needs plenty of room to reach and distribute the material, this method is frequently employed for large-scale projects. The mixed concrete is delivered on time and ready to use and thus it allows for a speedier and simpler application.
Benefits of Using Wet Mix Concrete
Wet mix concrete is a kind of free-flowing, non-shrink, high-strength pre-mix concrete mixture that provides several benefits, as follows:
- High Workability: The exceptional workability of wet mix concrete facilitates more effective placement, compaction, and finishing.
- Versatile Uses: It is quite flexible and appropriate for a wide range of real-world uses, including major construction projects.
- Consistent Quality: The completed concrete’s strength and durability are predictable due to the uniform mixing procedure, which guarantees consistent quality.
- Longer Workability: Wet mix concrete has a longer workability time, which allows for placement-related alterations, detailing, and corrections.
- Enhanced Compaction: It promotes appropriate compaction, resulting in uniformly packed concrete with little air space.
- Controlled Setting Time: Depending on the cement type and the surrounding circumstances, the setting time can be adjusted to satisfy project specifications.
Application of Wet Mix Concrete
Large-scale projects involving concrete foundations, slabs, columns, beams, and other structural components are best suited for wet pouring as this method facilitates continuous pouring and allows for effective concrete laying across large surfaces.
- Wet Mix Concrete in Foundation:
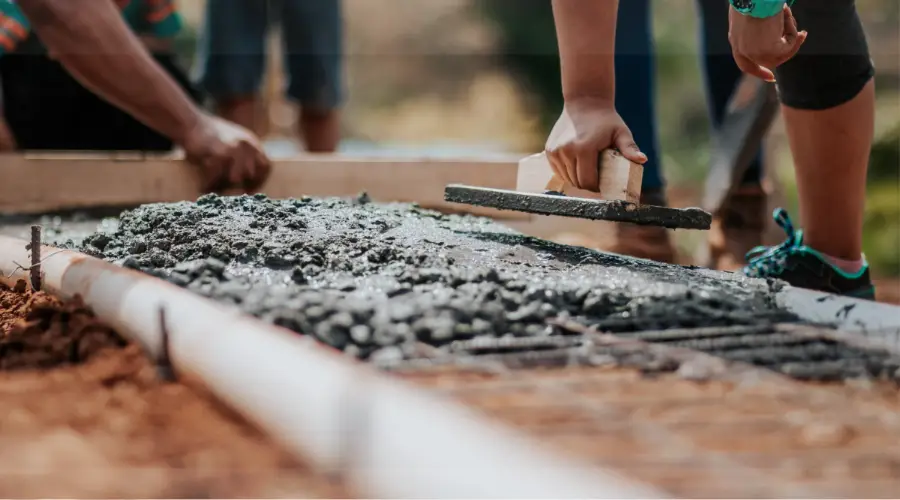

Due to its excellent workability and uniform consistency, wet mix concrete is frequently used in foundations to provide a sturdy base that satisfies load-bearing specifications.
- Wet Mix Concrete in Slabs:
It is perfect for pouring huge, homogenous slabs with smooth finishing, reducing cracks, and guaranteeing longevity because of its exceptional workability and long setting time.
- Wet Mix Concrete in Columns:
For the creation of sturdy, load-bearing columns with minimal air gaps, wet mix concrete offers uniform quality and enables precise compaction.
- Wet Mix Concrete in Beams:
Wet mix concrete is appropriate for beams because of its high strength and uniformity, which guarantee dependable load distribution and resistance to structural stresses.
- Wet Mix Concrete for Other Structural Components:
When consistency, strength, and longevity are crucial, wet mix concrete is utilised in a wide range of structural elements, such as walls, retaining walls, and precast components.
Mixing Process of Wet Mix Concrete
Wet concrete is produced in batch plants where it is mixed in highly efficient equipment in different batches. Before being delivered to the construction site, aggregates, cement, and water are mixed and blended in a wet batch concrete facility. This process guarantees that the mixture is prepared for usage right away after delivery. Wet batch facilities reduce wait times at building sites by pre-mixing the concrete, enabling speedy production and delivery. Workflows are accelerated, and overall efficiency is improved. These facilities are frequently used in commercial and industrial construction projects where time efficiency and a strong demand for concrete are essential. Pre-mixed concrete guarantees seamless construction without needless delays.
Due to its uniformity and consistency, the resulting wet mix is perfect for projects that call for exact and superior concrete composition. For large-scale projects or ones with strict quality standards, this method is particularly beneficial.
What is the Difference Between Wet-Mix & Dry-Mix?
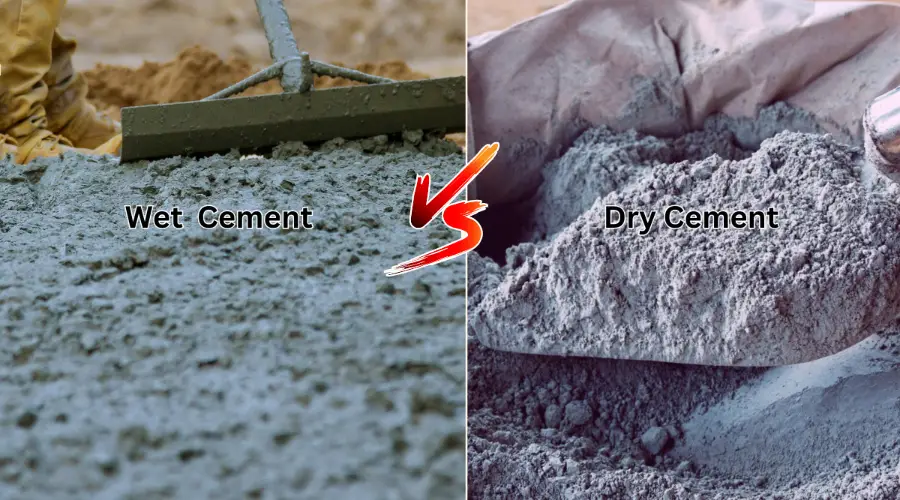
The main distinctions between wet and dry mix concrete are found in its application, storage duration, and outcomes:
| S.No | Aspect | Dry Mix Concrete | Wet Mix Concrete |
| 1 | Mixing Process | Ingredients are mixed without adding water until the time of placement. | Ingredients, including water, are fully mixed before transportation. |
| 2 | Water Content | Water is added at the construction site during placement. | Water is added during the mixing process at the plant. |
| 3 | Workability | Less workable initially; workability depends on the quantity of water added during placement. | More workable and consistent due to thorough pre-mixing with fixed quantities. |
| 4 | Equipment Dependency | It requires a mixer or equipment like a high-velocity hose to add water and mix on-site. | Relies on batching plant equipment for pre-mixing. |
| 5 | Environmental Impact | Can generate dust during dry mixing, which may impact air quality. | Reduced dust generation due to wet mixing in a controlled environment away from the actual construction site. |
| 6 | Setting Time | Starts setting after water is added on-site. | Begins setting soon after mixing at the plant. |
| 7 | Applications | Suitable for smaller projects or those requiring flexibility in water addition. | Ideal for large-scale projects needing consistent quality and rapid placement. |
| 8 | Precast Suitability | Less commonly used due to potential inconsistencies in the mix. | Preferred for precast applications due to the controlled mix design. |
| 9 | Quality Control | Quality can vary based on on-site mixing conditions. | Allows for better quality control at the plant. |
| 10 | Transportation | Easier to transport as dry mix is lighter and less time-sensitive. | Requires timely transportation to avoid setting during transit. |
| 11 | Storage Time | As dry mix concrete is made without water, it can be stored for a long period. | Wet mix concrete must be utilised within 24 hours after being mixed since it contains water. |
Conclusion
In summary, wet mix concrete is essential in modern construction and provides remarkable advantages like consistency, efficiency, and time savings. Many building projects require wet mix concrete, which is made in controlled batch processes and ensures high standards of quality.
FAQ’s
Yes. It is a great choice for large-scale projects where time efficiency and a strong demand for concrete are essential. Typically, these combinations are transported to the construction site with mixers and pumps from big trucks.
Wet pouring works well for large-scale concrete projects that include concrete slabs, columns, beams, foundations, and other structural elements. It makes it easier to pour continuously and enables efficient concrete laying on wide expanses.

